電漿粒團
(重定向自等离子体团)
電漿粒團是一種將電漿和磁場連接在一起的結構,並曾經被用來解釋像是球閃電的自然現象[1]、在磁層內的磁泡 [2],和彗尾內的物體,[3]、在太陽風[4][5]、在太陽的大氣層[6],和在太陽圈電流片。在實驗室內製造的電漿粒團包括逆轉磁場配置、Spheromaks、和密集電漿焦點。
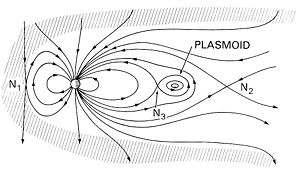
電漿粒團這個詞彙是在1956年由Winston H. Bostick (1916-1991)創造的,它的意思是"電漿-磁場個體"[7]:
電漿的散發不是無定形的一團,而是一種環形曲面的形式,我們將這個超環面結構稱為電漿粒團,它的意思是電漿-磁場個體。電漿粒團這個詞彙將使用於所有的電漿-磁場個體。
電漿粒團的特徵 编辑
Bostick寫道[7]:
電漿粒團看起來是朝著磁場方向被延長的電漿圓柱體,電漿粒團擁有可以測量的磁矩、可以測量的平均速度、一個橫斷的電場和可以測量的大小。電漿粒團彼此之間可以有交互作用,它們的軌道可能也被互相的扭曲。電漿粒團如果被拋出進入10−3mm汞柱壓力的氣體時,可以被做成螺旋狀和停止。電漿粒團也可能會互相摧毀成為碎片。但沒有足夠的證據支持它們會分裂和旋轉的假說。
宇宙論的應用 编辑
Bostick嘗試將它的電漿粒團理論應用在天文物理的現象上。他在1958年發表的論文[8],應用電漿相似的轉換使用電漿槍(密集電漿焦點裝置)讓一對電漿粒團槍互射,以這樣的交互作用模擬星系形成的一種早期模型[9][10]。
註解 编辑
- ^ Silberg, Paul A., "Ball Lightning and Plasmoids", (1962) Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 67, p.4941
- ^ Hones, E. W., Jr., "The magnetotail - Its generation and dissipation", (1976) Physics of solar planetary environments; Proceedings of the International Symposium on Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Boulder, Colo., June 7-18, 1976. Volume 2.
- ^ Roosen, R. G.; Brandt, J. C., "Possible Detection of Colliding Plasmoids in the Tail of Comet Kohoutek" (1976), Study of Comets, Proceedings of IAU Colloq. 25, held in Greenbelt, MD, 28 October - 1 November, 1974. Edited by B. D. Donn, M. Mumma, W. Jackson, M. A'Hearn, and R. Harrington. National Aeronautics and Space Administration SP 393, 1976., p.378
- ^ Lemaire, J.; Roth, M., Differences between solar wind plasmoids and ideal magnetohydrodynamic filaments (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) Planetary and Space Science, Volume 29, Issue 8, p. 843-849
- ^ Wang, S.; Lee, L. C.; Wei, C. Q.; Akasofu, S.-I., A mechanism for the formation of plasmoids and kink waves in the heliospheric current sheet (1988) Solar Physics (ISSN 0038-0938), vol. 117, no. 1, 1988, p. 157-169.
- ^ Cargill, P. J.; Pneuman, G. W., "The energy balance of plasmoids in the solar atmosphere" (1986), Astrophysical Journal, Part 1 (ISSN 0004-637X), vol. 307, Aug. 15, 1986, p. 820-825.
- ^ 7.0 7.1 Bostick, Winston H., "Experimental Study of Ionized Matter Projected across a Magnetic Field (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)", (1956) Physical Review, vol. 104, Issue 2, pp. 292-299
- ^ Bostick, Winston H., "Possible Hydromagnetic Simulation of Cosmical Phenomena in the Laboratory (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)" (1958) Cosmical Gas Dynamics, Proceedings from IAU Symposium no. 8. Edited by Johannes Martinus Burgers and Richard Nelson Thomas. International Astronomical Union. Symposium no. 8, p. 1090
- ^ W. L. Laurence, "Physicist creates universe in a test tube," New York Times, p. 1, Dec. 12, 1956.
- ^ Bostick, W. H., "What laboratory-produced plasma structures can contribute to the understanding of cosmic structures both large and small" (1986) IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science (ISSN 0093-3813), vol. PS-14, Dec. 1986, p. 703-717.
參考資料 编辑
- Bostick, W. H., "Experimental Study of Plasmoids (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)", Electromagnetic Phenomena in Cosmical Physics, Proceedings from IAU Symposium no. 6. Edited by Bo Lehnert. International Astronomical Union. Symposium no. 6, Cambridge University Press, p.87