細胞增殖
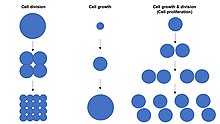
细胞增殖是指细胞生长和分裂成两个子细胞的过程[1][2][3][4]。细胞增殖使细胞数量成倍增加,因此它是组织生长的快速机制。细胞增殖要求细胞生长和细胞分裂同时发生,以使细胞的平均大小保持不变。细胞增殖与细胞生长或细胞分裂不同的是,细胞分裂時可以不发生细胞生长,這樣會生成许多小細胞(如卵裂),而细胞生长可以不发生细胞分裂,因而會产生单个较大的细胞(如神經元的生长)[5]。细胞总数由细胞增殖率减去细胞死亡率所决定。
参考 编辑
- ^ Conlon, Ian; Raff, Martin. Size Control in Animal Development. Cell. 1999, 96 (2): 235–244. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 9988218. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80563-2.
- ^ Grewal, Savraj S; Edgar, Bruce A. Controlling cell division in yeast and animals: does size matter?. Journal of Biology. 2003, 2 (1): 5. ISSN 1475-4924. PMID 12733996. doi:10.1186/1475-4924-2-5.
- ^ Neufeld, Thomas P; de la Cruz, Aida Flor A; Johnston, Laura A; Edgar, Bruce A. Coordination of Growth and Cell Division in the Drosophila Wing. Cell. 1998, 93 (7): 1183–1193. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 9657151. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81462-2.
- ^ Thompson, Barry J. Developmental control of cell growth and division in Drosophila. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2010, 22 (6): 788–794. PMID 20833011. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2010.08.018.
- ^ Saucedo, L. Why size matters: altering cell size. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 2002, 12 (5): 565–571. ISSN 0959-437X. PMID 12200162. doi:10.1016/S0959-437X(02)00341-6.