伸展構造
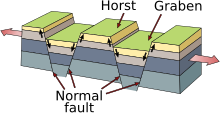
伸展構造(英語:Extensional tectonics)是指在地殼或岩石圈受張力而造成的構造。通常在大陸裂谷 [1]. 中洋脊,弧後盆地,分離板塊邊緣和被動邊緣等皆能形成伸展構造[2]。最常見的是在鏟形斷層内的滾動背斜(英語:rollover anticline)和背脊塌垮地塹[3]。在走滑斷層也有伸展構造,如伸展走滑體系(英語:releasing bends of strike-slip fault)。它是當走滑斷層沿走向錯開時,中間的間隙,會產生了一個延伸或擴張帶[4]。在聚合板塊邊緣,通常伸展構造較少,但當大陸碰撞時,地殼增厚擡升,由於重力垮塌,向側延申也形成伸展構造[5] [6]。
參考文獻 编辑
- ^ Kearey, P.; Klepeis, K.A.; Vine, F.J. (2009). "Continental rifts and rifted margins". Global Tectonics. WileyBlackwell. p. 153. ISBN 978-1-4443-0322-3
- ^ Park, R. G. (1997). Foundations of Structural Geology (3rd ed.). Psychology Press. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-7487-5802-9
- ^ White, R. S.; Hardman, R. F. P.; Watts, A. B.; Whitmarsh, R. B.; Ebinger, C. J.; Jackson, J. A.; Foster, A. N.; Hayward, N. J. (15 April 1999). "Extensional basin geometry and the elastic lithosphere". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 357 (1753): 741–765. doi:10.1098/rsta.1999.0351. JSTOR 55068
- ^ Armijo, R.; Meyer, B.; Navarro, S.; King, G.; Barka, A. (2002), "Asymmetric slip partitioning in the Sea of Marmara pull-apart: a clue to propagation processes of the North Anatolian Fault?" (PDF), Terra Nova, Wiley-Blackwell, 14 (2): 80–86, Bibcode:2002TeNov..14...80A, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.546.4111, doi:10.1046/j.1365-3121.2002.00397.x
- ^ Dunlap, J. W.; Fossen, H. (1998). "Early Paleozoic orogenic collapse, tectonic stability, and late Paleozoic continental rifting revealed through thermochronology of K-feldspars, southern Norway" (PDF). Tectonics. 17 (4): 604–620. Bibcode:1998Tecto..17..604D. doi:10.1029/98TC01603
- ^ Hartz, E. H.; Andresen, A.; Hodges, K. V.; Martin, M. W. (July 2000). "U–Pb and 40Ar/39Ar constraints on the Fjord Region Detachment Zone: A long-lived extensional fault in the central East Greenland Caledonides" (PDF). Journal of the Geological Society. 157 (4): 795–809. doi:10.1144/jgs.157.4.795. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-02