File:Changes in aragonite saturation of the world's oceans, 1880-2012 (US EPA).png
Changes_in_aragonite_saturation_of_the_world's_oceans,_1880-2012_(US_EPA).png (661 × 454 像素,檔案大小:138 KB,MIME 類型:image/png)
檔案歷史
點選日期/時間以檢視該時間的檔案版本。
| 日期/時間 | 縮圖 | 尺寸 | 使用者 | 備註 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目前 | 2019年12月29日 (日) 00:11 |  | 661 × 454(138 KB) | Epipelagic | reinstate title |
| 2019年12月28日 (六) 20:53 |  | 661 × 420(134 KB) | Epipelagic | crop | |
| 2013年2月22日 (五) 09:26 | 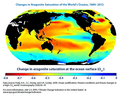 | 670 × 536(115 KB) | Enescot | {{Information |Description ={{en|1=This map shows changes in the amount of aragonite dissolved in ocean surface waters between the 1880s and the most recent decade (2003-2012). Aragonite is a form of [[:en:calcium car... |
檔案用途
下列2個頁面有用到此檔案:
全域檔案使用狀況
以下其他 wiki 使用了這個檔案:
- ar.wikipedia.org 的使用狀況
- en.wikipedia.org 的使用狀況
- en.wikiversity.org 的使用狀況
- ja.wikipedia.org 的使用狀況
- mk.wikipedia.org 的使用狀況
- pt.wikipedia.org 的使用狀況
- vi.wikipedia.org 的使用狀況



