毛细胞
毛细胞(英文:Hair cell)是所有的脊椎动物中听觉系统和平衡系统的感觉接收器[1][2]。在哺乳动物中,听觉毛细胞位于内耳耳蜗的基底膜上的柯蒂氏器上[1][2][3]。它名字的由来是从细胞的顶端长出的一束硬纤毛,也就是“毛束”结构,它还延伸到耳蜗里充满液体的蜗管中[1]。
| 毛细胞 | |
|---|---|
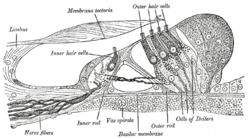 柯蒂氏器截面图 | |
 | |
| 基本信息 | |
| 位置 | 耳蜗 |
| 形态 | Unique (see text) |
| 神经递质 | Glutamate |
| Presynaptic connections | None |
| 标识字符 | |
| NeuroLex ID | sao1582628662, sao429277527 |
| 格雷氏 | p.1057 |
| 《神经解剖学术语》 [在维基数据上编辑] | |
分类
编辑功能
编辑毛束是声音的侦测器和放大器。过去几十年的研究表明:外毛细胞不直接把神经信号传递给大脑,而是机械地把传入耳蜗的低水平声音放大。这种放大作用可能是由毛细胞发束的运动造成的,也有可能是由毛细胞胞体的电学驱动的运动造成的。内毛细胞将耳蜗内液体的声音振动转化为电学信号,并通过听觉神经传递到听觉脑干,再到听觉皮层。
临床
编辑参见
编辑参考资料
编辑- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 McPherson, Duane R. Sensory Hair Cells: An Introduction to Structure and Physiology. Integrative and Comparative Biology. 2018-08-01, 58 (2): 282–300 [2021-03-13]. ISSN 1540-7063. doi:10.1093/icb/icy064. (原始内容存档于2020-10-18) (英语).
- ^ 2.0 2.1 Cochlear Hair Cell - an overview. Science Direct. [2021-03-13] (英语).
- ^ Journey into the world of hearing. www.cochlea.eu. [2021-03-13]. (原始内容存档于2021-04-13) (英语).
- ^ Purves, Dale; Augustine, George J.; Fitzpatrick, David; Katz, Lawrence C.; LaMantia, Anthony-Samuel; McNamara, James O.; Williams, S. Mark. Two Kinds of Hair Cells in the Cochlea. Neuroscience. 2nd edition. 2001 [2021-03-13]. (原始内容存档于2021-10-15) (英语).
- ^ Sensorineural hearing loss – See the signs, causes and treatment. www.hear-it.org. [2021-03-13]. (原始内容存档于2021-01-27) (英语).